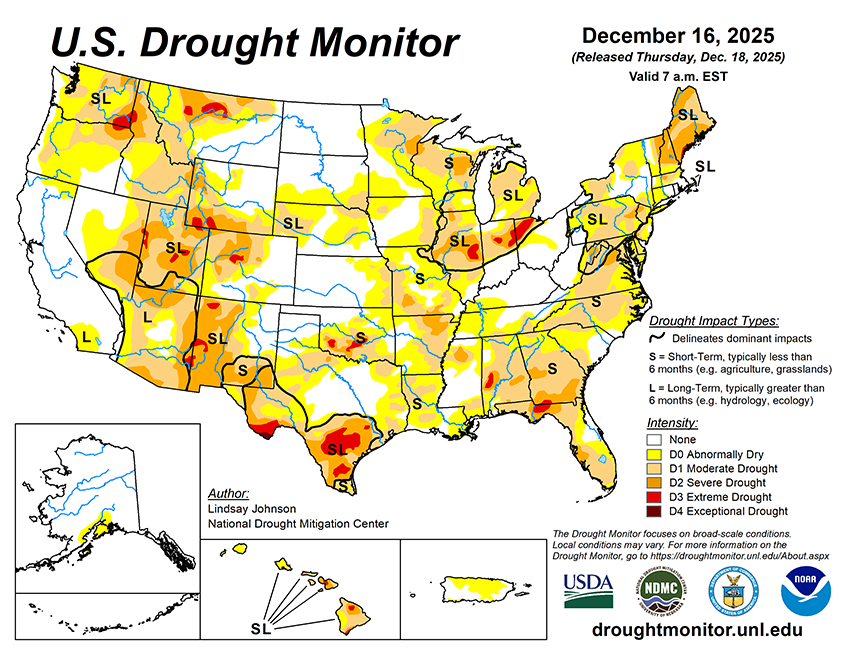
According to the National Weather Service’s 5-day (Dec. 18-23) quantitative precipitation forecast, the heaviest precipitation is forecast across the West, particularly along the Pacific Northwest coast and into northern California, where widespread totals may exceed 5 inches in some areas. Additional moderate to heavy precipitation is expected across the Cascades and into parts of the northern Rockies, with totals generally ranging from 1 to 4 inches. Lighter but still notable precipitation is forecast to extend eastward into portions of the central Rockies and the northern Plains. Across the central and eastern U.S., precipitation is expected to be more scattered and generally lighter. Portions of the Midwest, Ohio Valley, Southeast, and Gulf Coast may receive light to moderate precipitation, generally ranging from 0.5 to 2 inches. Farther east, a band of precipitation is indicated along parts of the East Coast, with locally higher amounts possible from the Southeast into the Mid-Atlantic and portions of the Northeast. Overall, the forecast highlights a wetter pattern in the West and more limited, variable precipitation across much of the central and eastern U.S.
The Climate Predictions Center’s 6 to 10 day temperature outlook (Dec. 22–26) shows an increased likelihood of above-normal temperatures across much of the central and southern U.S., extending from the West Coast through the Plains and into the Southeast. The highest probabilities for above-normal temperatures are centered over the southern Plains and Southwest, with much of the interior West, Rockies, and central Plains also favored to be warmer than normal. Near-normal temperatures are indicated across parts of the Pacific Northwest and the Great Lakes. Below-normal temperatures are most likely across portions of the Northeast, particularly northern New England, while Alaska shows a strong signal for below-normal temperatures across much of the state. Hawaii is favored to see above-normal temperatures during the period. In terms of precipitation, the 6 to 10 day outlook indicates an increased likelihood of above-normal precipitation across much of the West, including California, the Pacific Northwest, and parts of the Great Basin and northern Rockies. Near- to above-normal precipitation probabilities also extend into parts of the interior West. In contrast, below-normal precipitation is favored across much of the central Plains, lower Mississippi Valley, Southeast, and Florida, with the strongest signal centered over the southern Plains and Gulf Coast region. Near-normal precipitation probabilities are indicated across parts of the Great Lakes and Northeast, while Alaska shows mixed signals, with below-normal precipitation favored in southern portions and near-normal conditions elsewhere.