National Current Conditions... July 23rd thru July 29th

This week, drought worsened in the Northwest, Great Basin, and Rockies. Dryness and a bit of drought expanded in the Northeast and Southeast, while the Midwest saw improvements. The Plains had a mix of improvements and degradations.
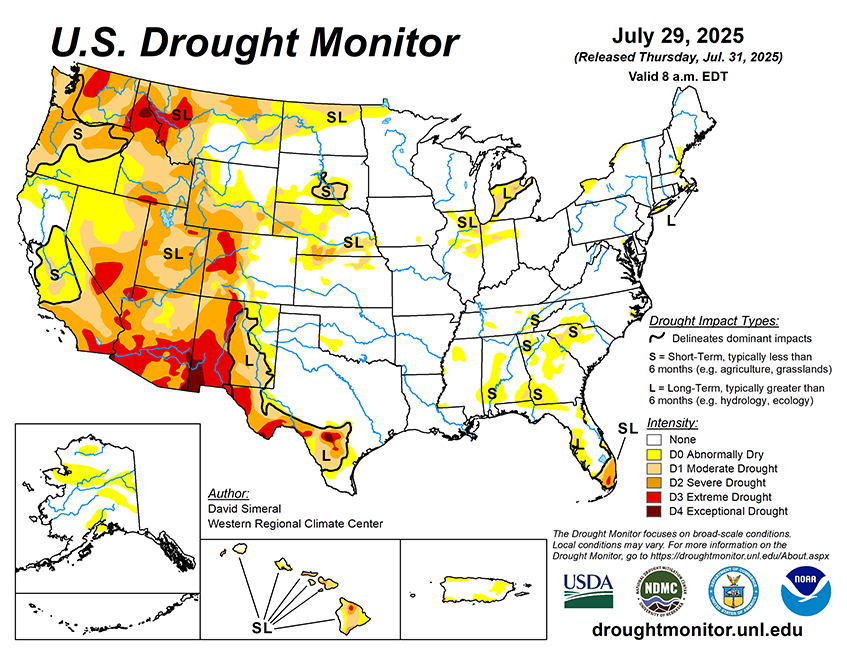
As of July 29, 2025, 26.01% of the U.S. and Puerto Rico and 31.02% of the lower 48 states are in drought, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor.

This Week's Drought Summary…
This U.S. Drought Monitor (USDM) week saw continued improvement in drought-related conditions across areas of the Midwest (Michigan, Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Minnesota), central and northern Plains (Kansas, Nebraska, Dakotas, eastern Montana), South (Texas), and in the Desert Southwest (New Mexico). During the past week, the most significant rainfall accumulations were observed across areas of Kansas, Missouri, Iowa, and Minnesota, where they ranged from 3 to 7+ inches. Elsewhere, short-term precipitation shortfalls (past 30 to 60 days) led to continued expansion of Abnormally Dry (D0) areas across the Southeast states including the Carolinas, Georgia, and Alabama as well as the introduction of isolated areas of Moderate Drought (D1) in Alabama, Georgia, and South Carolina where agriculture-related drought impacts are being reported. In the South, drought conditions continued to improve in western portions of Texas as well as in areas of eastern New Mexico where monsoonal storms have provided some minor relief to areas experiencing long-term drought. In the West, conditions continued to deteriorate across the Pacific Northwest (Oregon, Washington, Idaho) and areas of the Intermountain West (Wyoming, Utah, and Colorado), while areas of eastern Montana saw improvement in drought in response to precipitation events during the past few weeks. In terms of reservoir storage in the West, California’s major reservoirs continue to be at or above historical averages for the date (July 29), with the state’s two largest reservoirs, Lake Shasta and Lake Oroville, at 105% and 116% of average, respectively. In the Southwest, the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation is reporting (July 27) Lake Powell at 32% full (46% of average), Lake Mead at 31% full (51%), and the total Colorado system at 39% of capacity (compared to 44% of capacity the same time last year).