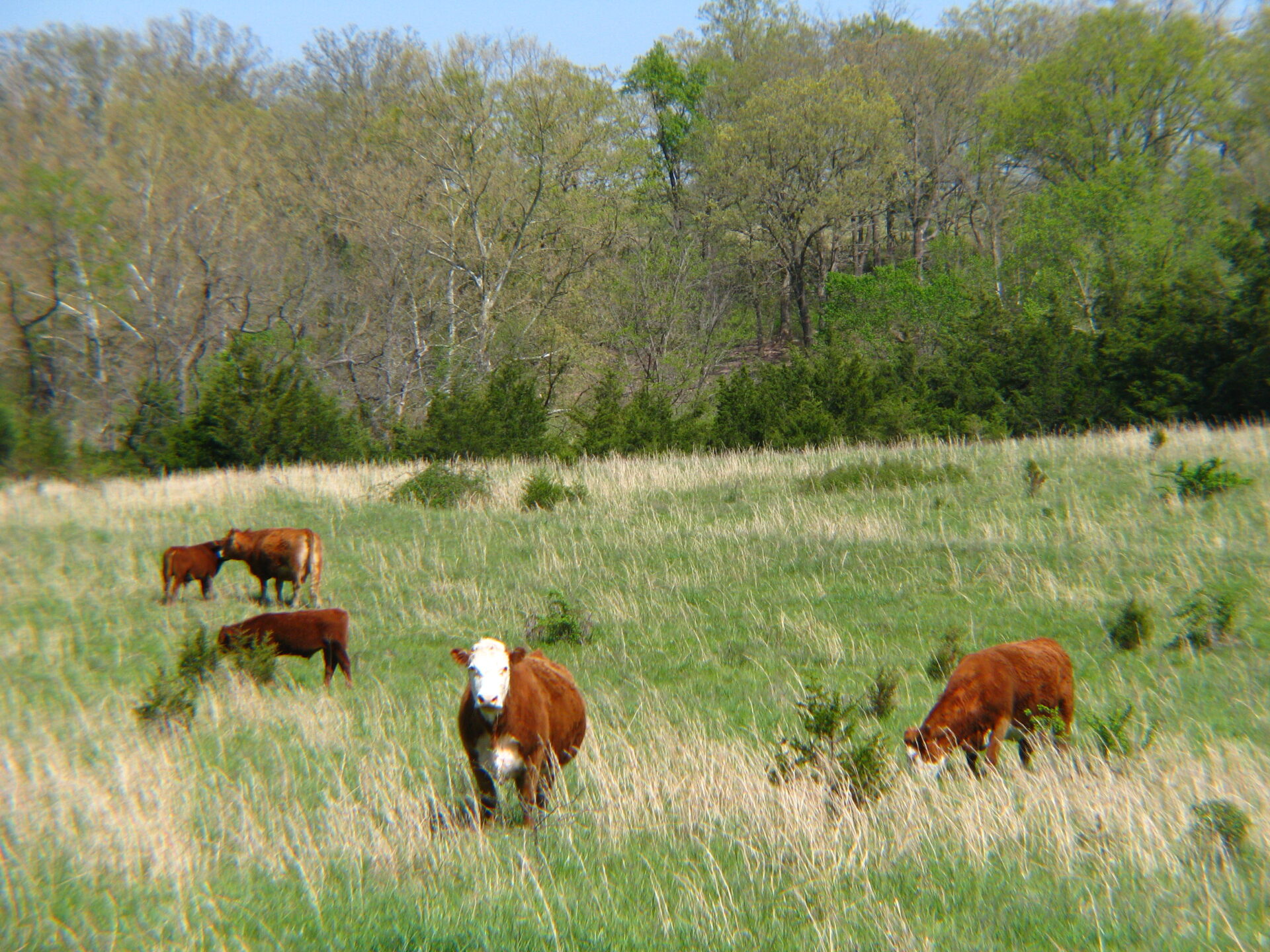
Cattle on pasture in the Missouri Ozarks. (Photo: Julie A Brown)
Source: Robert Langellier
America’s “fescue belt,” named for an exotic grass called tall fescue, dominates the pastureland from Missouri and Arkansas in the west to the coast of the Carolinas in the east. Within that swath, a quarter of the nation’s cows — more than 15 million in all — graze fields that stay green through the winter while the rest of the region’s grasses turn brown and go dormant.
But the fescue these cows are eating is toxic. The animals lose hooves. Parts of their tails and the tips of their ears slough off. For most of the year, they spend any moderately warm day standing in ponds and creeks trying to reduce fevers. They breathe heavily, fail to put on weight, and produce less milk. Some fail to conceive, and some of the calves they do conceive die.
The disorder, fescue toxicosis, costs the livestock industry up to $2 billion a year in lost production. “Fescue toxicity is the most devastating livestock disorder east of the Mississippi,” said Craig Roberts, a forage specialist at the University of Missouri Extension, or MU, and an expert on fescue.
By the early 20th century, decades of timber-cutting and overgrazing had left the ranching region in southern states barren, its nutrient-rich native grasses replaced by a motley assortment of plants that made poor forage. Then, in the 1930s, a University of Kentucky professor spotted an exotic type of fescue growing in the mountains of eastern Kentucky, which seemed to thrive even on exhausted land. Unlike most native grasses, Kentucky-31, as it was called, stayed green and hearty through the winter. Ranchers found the species remarkably resilient and, if not beloved by cattle, edible enough to plant. Over the next 20 years, much of the country’s southern landscape was transformed into a lush, evergreen pasture capable of supporting a robust cattle industry.
As early as the 1950s, however, ranchers began to notice tall fescue’s disturbing effects: One study showed that cattle had to be fenced out of other grasses before they’d touch fescue. When they did eat it, the cows saw only one-sixth of their normal weight gain and lost eight pounds of milk production a day.
Between the cells in fescue grows an endophyte, a fungus living symbiotically inside the grass. The endophyte is what makes the fescue robust against drought and overgrazing, but it’s also what makes it toxic. When scientists engineered a version of fescue without the fungal endophyte, in 1982, its hardiness disappeared and ranchers saw it die out among their winter pastures. Farmers learned to live with the health impacts of the toxic version, and today it remains the primary pasture grass across 37 million acres of farmland.
It’s a longstanding problem, and it’s spreading. Warming temperatures from climate change are now expanding the northern limit of the fescue belt, and the grass is marching into new areas, taking root on disturbed land, such as pastures. Northern Illinois and southern Iowa could already be officially added to the fescue belt, Roberts said, introducing toxicosis to new farming regions.
“It’s becoming not just present but part of their normal pastures,” he said, noting that he increasingly gets calls from farmers in this region who are wondering what to do.
As more farmers find themselves facing the challenges of toxic fescue, there are two strategies emerging to finally solve the decades-old problem, though in diametrically opposed ways. One involves planting a modified version of tall fescue — called “friendly fescue” — in which the toxic endophyte has been replaced by a benign one that still keeps the grass hearty and green all winter. Another would abandon fescue altogether and restore the native grasses and wildflowers that once dominated the region, as well as help revitalize natural carbon sinks and fight climate change.
For a variety of reasons — some economic, some cultural — neither solution has really taken hold with most fescue belt ranchers. But the debate embodies the agricultural industry in the era of climate change: As ecosystems shift and extreme weather makes farming even more precarious, ranchers are facing tough decisions about how to adapt their land use practices. What is best for business, and will that ultimately be what’s best for the land and for the changing climate?
Friendly fescue hit the market in 2000, developed by Pennington Seed Inc. It looks identical to toxic fescue and behaves almost identically, thus requiring little change to the ranching habits of fescue belt farmers over the last 70 years.
It would seem an ideal fit for an industry focused on maintaining the status quo amid climate challenges. But ranchers have been slow to embrace it. For one thing, friendly fescue, formally known as “novel endophyte fescue,” costs twice as much as the toxic variety — $4 for a pound of seed versus $2. And replacing one grass with another is labor-intensive; a 2004 report by the University of Georgia said it would take farmers who made the switch about three years to break even. Matt Poore, a professor of animal science at North Carolina State University, chairs the Alliance for Grassland Renewal, a national organization dedicated to eradicating toxic fescue. Yet Poore, who also raises cattle, has only converted 30 percent of his fields, preferring to do it slowly. “The fear of failure is a big deal,” he said. “You’re sticking your neck out there when you go to kill something that looks really good.”
Many farmers would like to avoid the risk of total pasture makeovers, if they can. Until now, toxic fescue ranchers have found ways to scrape by, and a parade of treatments have come out through the decades, promising relief from toxicosis.
They can supplement their cows’ diets with grain (an expensive remedy), or cut and dry their fescue and feed it to them as hay, which reduces its toxicity somewhat. They can dilute the toxicity of their fields by planting clover among the fescue, or clip the especially toxic seed heads before cows can graze them. They can try to genetically select cows with moderate fescue tolerance, which can salvage as much as a quarter of their losses.
Poore counts over 100 such remedies. “If you do enough of those things you can tell yourself you don’t really have a problem,” he said. Meanwhile, the lush ground cover that fescue displays in winter is seductive.
A lack of trust, too, is a problem. In the early 1980s, when researchers introduced endophyte-free fescue, it was hailed as the answer to toxicosis, a way to save the industry. Ranchers trusted the scientists, and they lost a lot of money when that version withered in the fields. The sting of that debacle persists as researchers try to convince ranchers to trust friendly fescue. “The sins of the past have come back to haunt us,” MU’s Roberts said. “It’s going to take a while to overcome that screwup.”
Every March, Roberts and other scientists travel around the fescue belt giving workshops on friendly fescue to anyone who will listen. He tries to assuage farmers who are worried about the expense and labor of pasture conversion.
There aren’t good numbers on adoption rates, because seed companies are guarded about how much they sell. But Robert says he knows it’s rising. Some states promote it more than others, by offering cost-shares, for example, and hosting workshops like those Roberts leads.
It doesn’t help that endophyte-free fescue — the one that fails in the winter — remains on the market. The state of Kentucky even provides cost-share funding for ranchers who switch from toxic fescue to endophyte-free fescue. And several Kentucky ranchers said they were still unclear on the differences among toxic fescue, endophyte-free fescue, and friendly fescue. Farm supply stores often don’t even stock friendly fescue seed, as it’s less shelf stable.
Roberts noted that toxic fescue exudes fluids that “pretty much destroy the food web,” poisoning insects that quail and other creatures feed on. A 2014 study showed that climate change could increase the endophyte’s toxicity. Friendly fescue soil, by contrast, has more microbes than toxic fescue soil. And water quality is better with friendly fescue, since sick cows don’t have to congregate in streams and ponds to stay cool.
Despite the confusion and slow uptake, Roberts is optimistic, noting the 30 years it took for farmers to embrace the revolution of hybrid corn in the early 20th century. And he can point to some wins. Darrel Franson, a Missouri rancher who remembers the endophyte-free fescue debacle, nevertheless decided to take the risk, converting his 126 acres to friendly fescue. He loves the results. “It’s hard to argue with the production potential of tall fescue and the length of season it gives us,” he said.
Roberts’ employer, the University of Missouri, is betting that a modified version of exotic fescue will appeal to ranchers more than the idea of converting to native grasslands. “What we’re promoting is environmentally friendly as well as economically sound,” he said. “When you seed a nontoxic endophyte and add legumes [to dilute pasture toxicity], that works as well as anything, and we have a lot of data on it. It may take another 20 years for it to catch on, but it’s not going away. It’s too good.”
For decades, Amy Hamilton and her late husband, Rex, fought fescue toxicosis in Texas County, Missouri, the heart of the Ozarks. They watched their and their neighbors’ cows lose tail switches, hooves, and parts of their ears to gangrene. Finally, they’d had enough.
But the Hamiltons didn’t reach for an artificially modified version of an exotic grass. Instead, in 2012, they converted 90 acres of pasture to native warm-season grasses, using their own money and cost-share funding from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Natural Resources Conservation Service, or NRCS. The effects were immediate; the next year they documented increased conception and weaning rates in their cows and calves. Since then, they’ve converted another 75 acres. A former soil conservationist with a degree in agronomy, Hamilton’s mission became to annihilate fescue, on her property and across the fescue belt.
I visited Hamilton’s ranch in November 2022. She and her family run about 45 cows and 150 bison. She and her daughter Elizabeth Steele, who helps run the family’s native seed company, walked through a pasture where fescue grew 15 years ago. Now big bluestem, little bluestem, and sunflowers fill the main body of the pasture, and freshwater cordgrass and ironweed decorate a creek’s edge. Quail have returned for the first time in decades.
Unlike the Hamiltons’ neighbors’ pastures, however, this field was not green; most of the plants had gone dormant for winter. Hamilton reached through a thick mass of bluestem and pointed to two diminutive, green plants: wild rye and a sedge species, cool-season grasses that provide a native analogue to fescue — and, crucially, winter forage.
“This is what would have been here pre-settlement,” said Steele, referring to the land before Europeans arrived. “A functioning grassland with different plants serving different functions. Nature’s design is not for monocultures.”
To understand the fescue-native debate requires an understanding of the ecological tradeoff between warm- and cool-season grasses. Simply put, warm-season grasses grow in the summer, harnessing the strong sunshine to grow tall and robust; then they go dormant in the winter. Cool-season grasses do the opposite, putting their evolutionary resources into frost-tolerance. As a result, they tend to be smaller than their warm-season counterparts, providing less biomass and less food per plant for the cows that graze them.
Hamilton and Steele have decided to bet on biodiversity. Instead of a year-round monoculture of fescue, they have a biodiverse mix of warm- and cool-season grasses, along with wildflowers. It’s not as visibly lush as a fescue field, but the benefits to cattle health, soil health, and climate resistance make it worth it. “It is a kind of faith that these prairies evolved for the good of the native species that were here,” Hamilton said.
Even with the leaner cool-season grasses, their native fields produce twice as much forage as the old fescue fields and generate a much higher amount of organic matter, enriching the soil and allowing the pasture to hold more water. A soil-health specialist from NRCS tested their soil’s organic matter content before the 2012 restoration, then again five years later. The result was pastureland that holds up to a half gallon more water than a typical fescue field.
In a warming climate with more extreme droughts — much of the Ozarks was in severe drought last year — that extra water storage can make a critical difference for cattle and soil health. The southeastern U.S., the heart of the fescue belt, faces a future of more intense drought and floods. The Hamiltons’ biodiverse style of ranching helps address both extremes, and they expect their native ecosystems will be more resilient to climate change.
“The extra water trickles into our stream through the year, as opposed to running off in a flood,” said Steele.
The roots of native grasses also reach three times deeper than fescue roots, making them drought-resistant as well as efficient carbon sinks. Grasslands are uniquely good at carbon sequestration. Unlike forests, they store more than 80 percent of their carbon underground, where it’s more safely sequestered than in aboveground trees where the carbon can potentially volatilize and return to the atmosphere.
What’s more, intensive grazing of monocultures makes it hard to sequester carbon. A 2019 study, published in the journal Nature, showed that native, biodiverse, restored grasslands hold more than twice as much carbon as monocultures. The deep roots of the Hamiltons’ native species lock carbon deep underground, where it can take hundreds or even thousands of years to return to the atmosphere.
In the years since the Hamiltons converted their fields, the use of native warm-season grasses has gained momentum in the ranching industry. The University of Tennessee — firmly in the fescue belt — opened the Center for Native Grasslands Management in 2006 aimed at getting ranchers to incorporate native warm-season grasses, known as NWSGs, into pastureland. The Missouri Department of Conservation conducts workshops to familiarize ranchers with NWSGs. Research by the center found that pastures of native switchgrass financially outperform fescue pastures.
And Patrick D. Keyser, the center’s director, says native grasses significantly outperform fescue in climate resiliency. Fescue, he says, wants it to be 73 degrees and rainy every other day. “Think Oregon or Scotland,” he said. Native warm-season grasses in the fescue belt, on the other hand, can go weeks with blistering heat and drought without a problem. “To them, the worst climate projections that we’re getting really aren’t a big deal. From a resiliency standpoint, they absolutely win.”
If replacing fescue with natives is moving slowly in general, replacing it with native cool-season grasses, to get year-round forage, remains nearly unheard of. As with friendly fescue, cost is partly to blame. Elizabeth Steele’s “cowboy math” estimates that a native conversion today would cost around $365 per acre, a scary number for ranchers.
Proponents of native conversion also face a more complicated obstacle than cost as they seek buy-in from ranchers. The debate over how beef cattle are raised is caught up in the culture war over climate change. By some estimates, meat production accounts for nearly 60 percent of the greenhouse gases generated by the food system, with beef as the leading culprit. Even as the concept of “regenerative ranching,” a method of cattle farming that tries to restore degraded soil and reduce emissions, has secured a toehold in the industry, “climate change” remains a political term in farm country, one that is largely avoided.
Ranchers like Amy Hamilton risk being marginalized as “progressives.” So while she believes diverse native grasslands will make pastures more resilient to climate change, she doesn’t mention that when proselytizing to fellow ranchers. Insead, she talks about increased water infiltration, more abundant wildlife, and improved soil health — things that matter to ranchers no matter their thoughts on climate change.
She also tells them that native conversion pencils out. Hamilton doesn’t fertilize her pastures, and she rarely uses hay, as most ranchers do to supplement their cows’ fescue diet. And Steele estimates that, because native pastures produce more forage than fescue monocultures, increased forage and resulting weight gain makes up for the initial conversion costs in less than two years. “The more you emulate natural systems, the less money you have to spend on stuff like baling machines, herbicides, toxicosis effects, and fertilizer,” she said. That extra forage also allows ranchers to feed more cows. So if a rancher wants to expand their herd size, they can either expand their fescue acreage, for $3,000 an acre, or spend $365 an acre to convert the land they already have to natives.
Saving money matters in the fescue belt. According to U.S. Department of Agriculture data, 60 percent of farms in Texas County, Missouri, run a deficit, and every state in the fescue belt loses money on agriculture, except for Illinois, which is largely a crop state.
“Agriculture is so hard that if you don’t do it with your pocketbook in mind, you can cause people to go broke. I don’t want to do that,” Hamilton said.
Hamilton estimates that more than 100 other fescue belt ranchers she’s in touch with are in the process of converting some or all of their pasture to native grasses. One of them, Steve Freeman, co-owns Woods Fork Cattle Company with his wife, Judy, in Hartville, Missouri. Freeman has converted 80 acres of fescue to natives, with plans to convert 180 more in three years. In total, that will make a third of his pasture diverse native grasslands.
“Almost all my inspiration has come from going to [the Hamiltons’] field days every year and seeing what this land could be,” Freeman told me on the phone. For him it’s not just about eradicating fescue toxicosis, it’s about the whole suite of benefits for biodiversity, soil health, and water retention. “I realized we’re not going to get there with the grasses we have.”
Freeman notes the power imbalance between the informal effort to promote native grasses and the universities and beef industry groups that are pushing modified fescue. “There’s no money that backs this,” he said of native restoration. “The novel endophytes and those kinds of things, there’s a lot of money to be made. They’ve helped the universities. I think [Hamilton] is starting to change people’s minds, but it’s been 15 years of doing this.”
For his part, MU’s Roberts hears the subtle dig at his work. “Friends of mine in conservation groups think the university professors are hooked on fescue,” he said. “They’re not. What they’re hooked on is a long grazing season, good yield, and good quality. They’re hooked on criteria, not on a species.”
Either way, change on this scale takes time. The University of Missouri claims that 98 percent of pastures in the state are still toxic, with ranchers slowly opening up to either friendly fescue or native forage. “I’m sure there are ranchers out there that think we’re absolutely nuts,” Hamilton said. “But some of them are interested in thinking about new ways of doing things.”
As we drove out to visit her cows, we passed some of her neighbors’ fields. In one, a herd of emaciated cattle had grazed a fescue field down to stubble. In another, all but a few cows stood in the middle of a pond, trying to cool themselves on a mild, cloudy day.
“These are good people,” Hamilton said. “They’re just trying to make a living.”