National Conditions: February 22, 2023 - February 28, 2023
California saw major drought improvements as the storms just keep coming. Most of the states in the West, Plains, and Midwest improved too. In contrast, Florida saw a major expansion of drought. Texas worsened too.
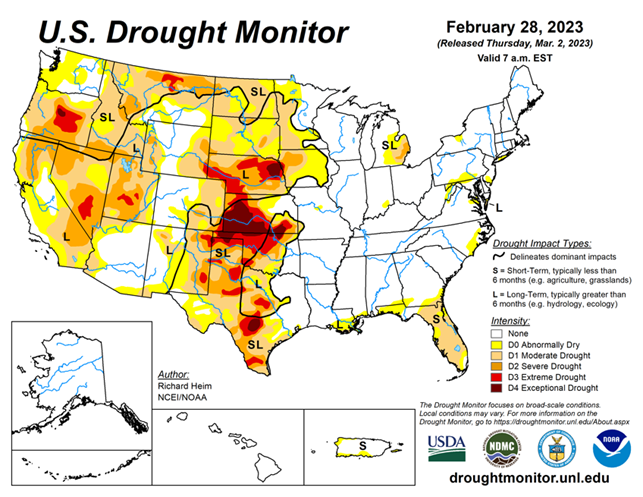
As of February 28, 2023, 32.13% of the U.S. and Puerto Rico and 38.46% of the lower 48 states are in drought, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor.

This Week's Drought Summary...
A series of Pacific low pressure and frontal systems moved across the western contiguous U.S. (CONUS) during this U.S. Drought Monitor (USDM) week (February 22-28). The weather systems dropped copious amounts of rain and snow across the West, especially over the Sierra and coastal ranges and Rocky Mountains. The weather systems re-intensified as they crossed the Plains and into the Midwest, tapping Gulf of Mexico moisture to spread several inches of rain over northeast Texas to the Appalachians and Ohio Valley, with several inches of snow falling in the below-freezing air across the northern tier states from the Dakotas to New England. A high-pressure ridge over the Gulf of Mexico generated a southerly flow that spread warmer-than-normal air from the Gulf Coast to southern Great Lakes. It also pushed the low-pressure systems along a storm track that went northeastward from the southern and central Plains to the Great Lakes.
Temperatures averaged cooler than normal across the snowy northern states, across the central to northern Plains, and over the West. Little to no precipitation fell across the Gulf Coast, western portions of the southern and central Plains, and over the northern Plains near the Canadian border. It was also drier than normal over parts of the Pacific Northwest, northern New England, and the Mid-Atlantic states. Wetter-than-normal conditions were widespread across the rest of the West, parts of the northern and central Plains and Northeast, and much of the Midwest. Drought or abnormal dryness expanded where it continued dry in parts of Texas, Florida, and other Gulf Coast states. Drought or abnormal dryness contracted or reduced in intensity where it was wet across much of California and other parts of the West and Plains, as well as part of the Great Lakes region.
Looking Ahead...
As this USDM week ended, one weather system was moving across the Northeast and another was slamming into the West. More Pacific weather systems will follow during March 2-7, bringing half an inch or more of precipitation to the West Coast and higher elevations of the West, parts of the Great Plains, and much of the CONUS to the east of the Plains. Another 4 inches or more of precipitation can be expected for the Sierra Nevada and coastal ranges, and from northeastern Texas and eastern Oklahoma to the Ohio Valley and southern Appalachians. An inch or more of precipitation should be widespread from eastern Kansas to the southern Great Lakes, and from the eastern Great Lakes to the Northeast and Mid-Atlantic states. Western and some central parts of the Great Plains, especially Nebraska, western Texas, and southeast New Mexico, as well as southern California to the Great Basin, are forecast to receive less than half an inch of precipitation. Temperatures are predicted to be warmer than normal in the south and southeast to cooler than normal in the West.
A cooler- and wetter-than-normal pattern is likely for March 8-15 across the CONUS. The Gulf of Mexico coast and much of Alaska likely begin this period warmer than normal, but odds favor cooler-than-normal temperatures as the period progresses. At the beginning of this period, below-normal precipitation is favored in the Northeast and Great Lakes, but below-normal precipitation is expected to dominate the southern half of Alaska through the period.














