Derrell S. Peel -- Oklahoma State University
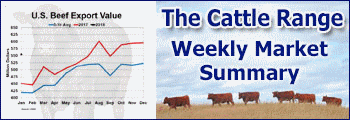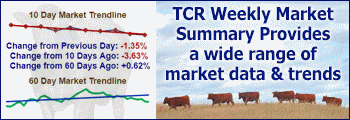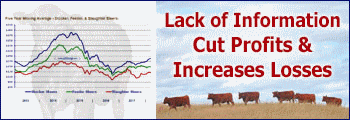
Through mid-April, beef cow slaughter is up 16.9 percent year over year; a surprisingly strong rate of cow slaughter for this time of year. This likely reflects continuing drought impacts carried over from last year, combined with very strong cull cow prices and limited forage prospects going forward. The fast pace of cow slaughter thus far implies the likelihood of significant beef cow herd liquidation in 2022. Liquidation is expected to continue in the first half of the year unless drought conditions improve immediately and significantly. Cow slaughter could moderate late in the year if early culling and overall lower cow numbers result in lower seasonal slaughter in the fall.
However, the numbers tell the story. The current pace of beef cow slaughter suggests an annual beef herd culling rate of 13.8 percent, a record in data back to 1986. The beef cow inventory would likely decrease by 4 percent year over year with the January 1, 2023, inventory dropping below 29 million head. This would be the largest annual beef cow herd decrease since the mid-1980s. The current beef cow slaughter pace will probably not continue all year. In order for annual beef cow slaughter to average, say 13 percent higher year over year, average beef cow slaughter for the remainder of the year would have to average 11.6 percent. In that example, net beef herd culling would still be over 13 percent this year. The result would likely be a January 1, 2023, beef cow inventory in the vicinity of 29.0 million head, down over 3.5 percent year over year. If annual beef cow slaughter equaled last year’s nine percent year over year increase, slaughter would have to average 6.1 percent higher year over year for the remainder of the year. That level of decrease in the slaughter rate (from the current 16.9 percent rate) seems unlikely at this point. In this case, the net herd culling rate would be just under 13 percent (though still a record level) and the 2023 beef cow herd could be roughly 29.2 million head, down about three percent year over year.
All of these outcomes depend on drought in the coming weeks and months. Dramatic and immediate improvement in drought conditions could allow the industry to avoid these rather dire results. The next few months will likely have impacts on the cattle industry for several years. Drought conditions that result in the levels of liquidation described above would also prevent retention of replacement heifers. This implies that, if conditions do not improve until late this year or into next year, better conditions in 2023 would, at best, allow the industry to stabilize inventories and lay the groundwork to begin recovery in 2024 at the earliest.